The Enzymes Called Blank Breaks Down the Substrate Called
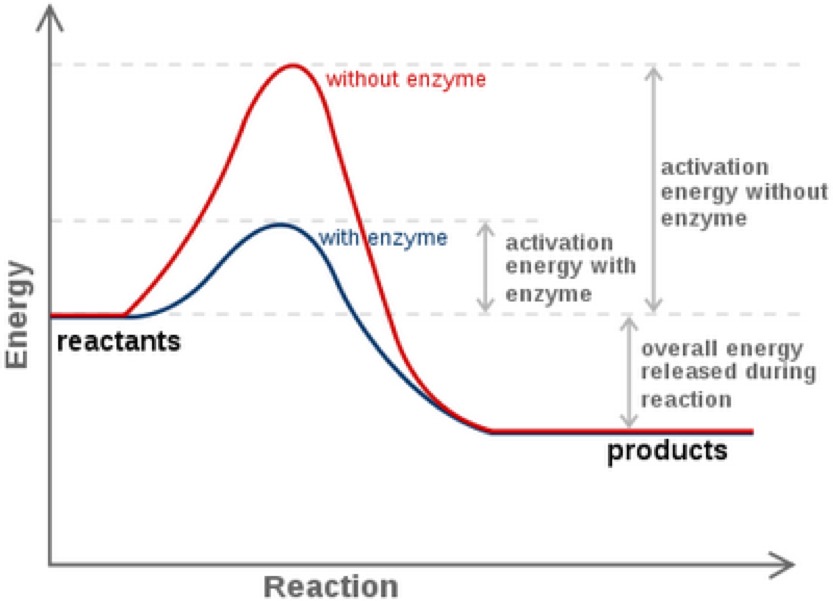
Hence by providing a surface for the substrate an enzyme slows down the activation energy of the reaction. They act only in the stomach lumen and do not digest intracellular proteins Several digestive enzymes are secreted as zymogens because.

Enzyme Function Ck 12 Foundation
An enzyme called amylase breaks down starches complex carbohydrates into sugars which your body can more easily absorb.
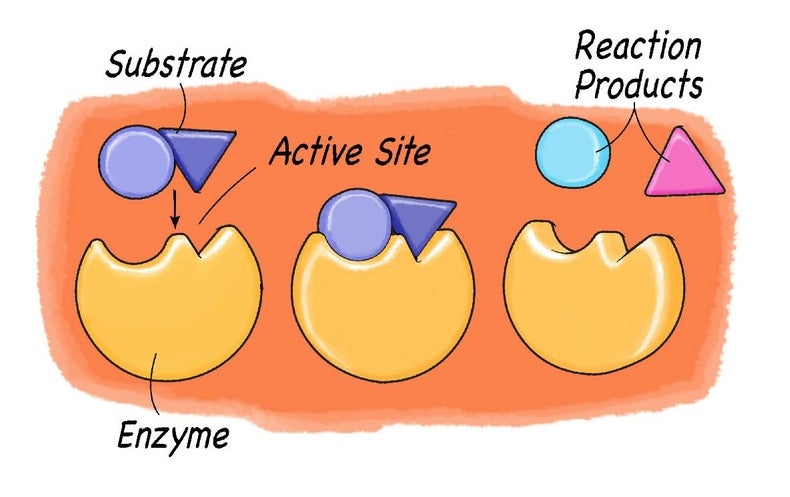
. Only molecules with exactly the right shape will bind to the enzyme and react. They do this by breaking down molecules the molecules that each enzyme breaks down are different and they are called the substrate. It breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids that can be easily absorbed in the small intestine.
Common suffix of enzymes enzymes are also named for the molecules they act upon. Enzyme Active Site and Substrate Specificity. By temporarily binding to the substrate an enzyme can lower the energy needed for a.
Enzymes work on substances called substrates. Enzymes are blank because they have a unique 3-D shape that only allows molecules that are the correct size and shape to make close contact. This is a very specific shape and the most important part of the.
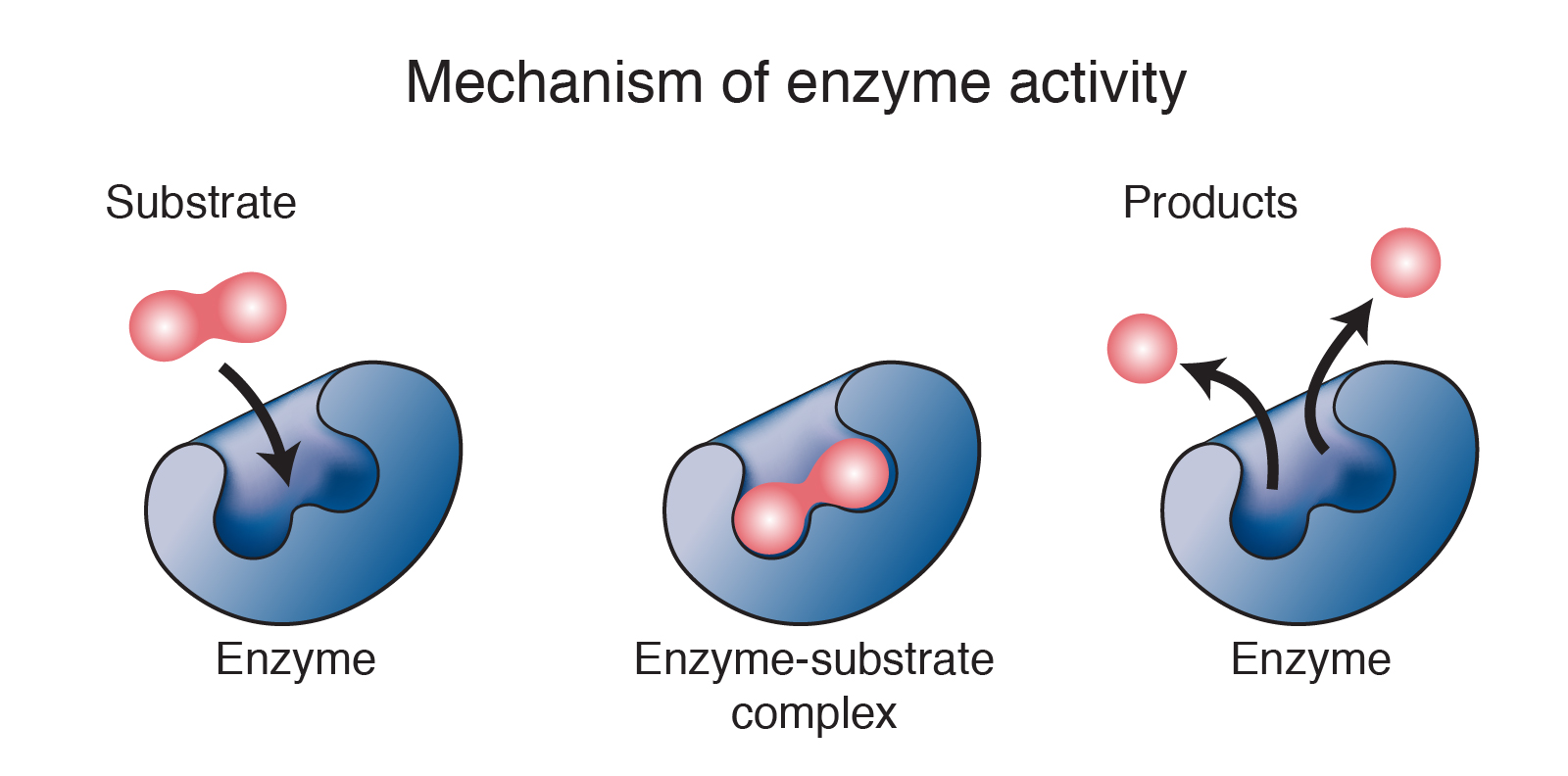
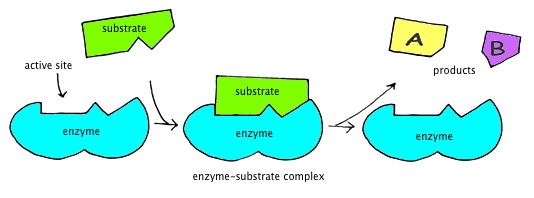
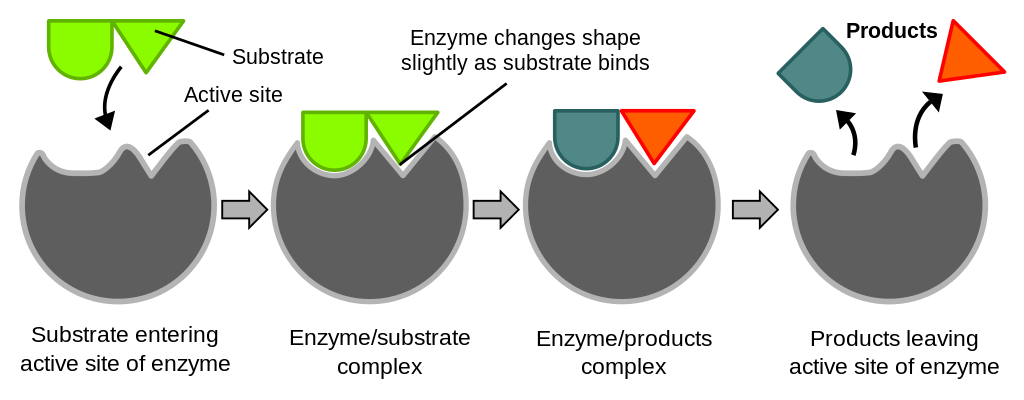
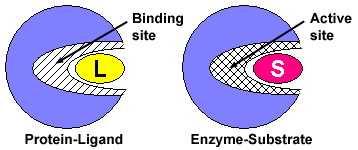
The enzyme attaches to the substrate molecule at a specific location called the active site. The enzymes called _____ breaks down the substrate called _____. The enzyme can be broken down into millions of parts and due to they are able to reusable and can change their shapes the change in the enzymes is called denaturation.
A condition known as dry mouth xerostomia occurs when you dont have enough saliva in your mouth. Proton force The _____ motive _____ describes the formation of a hydrogen ion gradient which powers ATP production using the electron transport system. With the aid of the enzyme lactase the substrate lactose is broken down into two products glucose and galactose.
The enzyme is taking the red substrate and turning it blue. Chemically they are proteinaceous in nature which act on substrates to give the end result of the reactions called products. The part of the enzyme to which the reactant binds attaches is called the active site.
Enzymes That Break Down Lipids. An enzyme ____ a chemical reaction without being changed itself. An enzyme that breaks down proteins to amino acids is called an _____.
The intermediate state where the substrate binds to the enzyme is called the transition state. Lipid is a biochemical word meaning fat In the course of your normal cellular function your body breaks down fats regularly. Enzymes are substances that play a crucial role in carrying out biochemical reactions.
The enzymes active site is blocked by a competitive inhibitor. Saliva also contains an enzyme called lingual lipase which breaks down fats. The substrate can bind to a specific place in the enzyme called the active site.
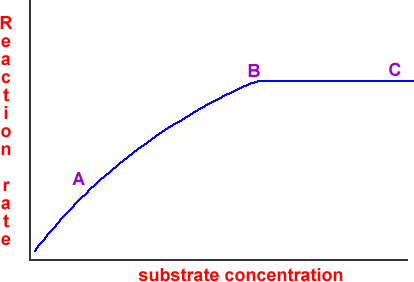
The enzyme cant function if too many substrates are trying to bind. A protein whose shape has been changed due to heat or harsh chemicals is known as a n ____ protein. Enzymes are very specific about which reactions they catalyze.
This can make it difficult for you to chew. The enzymes that can selectively cut DNA at specific locations during various types of genetic recombination are called. The enzymes that are required to break down arabinose will be produced after ___ binds to the araC protein causing araC to change its shape.
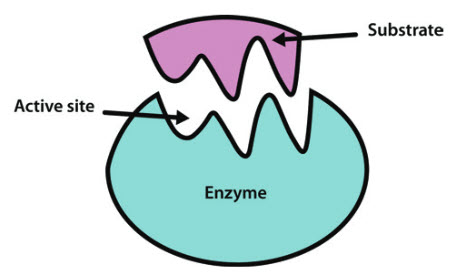
These are the reactant or substrate molecules. The reaction takes place on the part of the enzyme called the active site. How does an enzyme work.
Thus for any type of chemical reaction. While lipases break down lipids carbohydrases break down carbohydrates. The fastest enzyme which breaks down hydrogen peroxide in the liver.
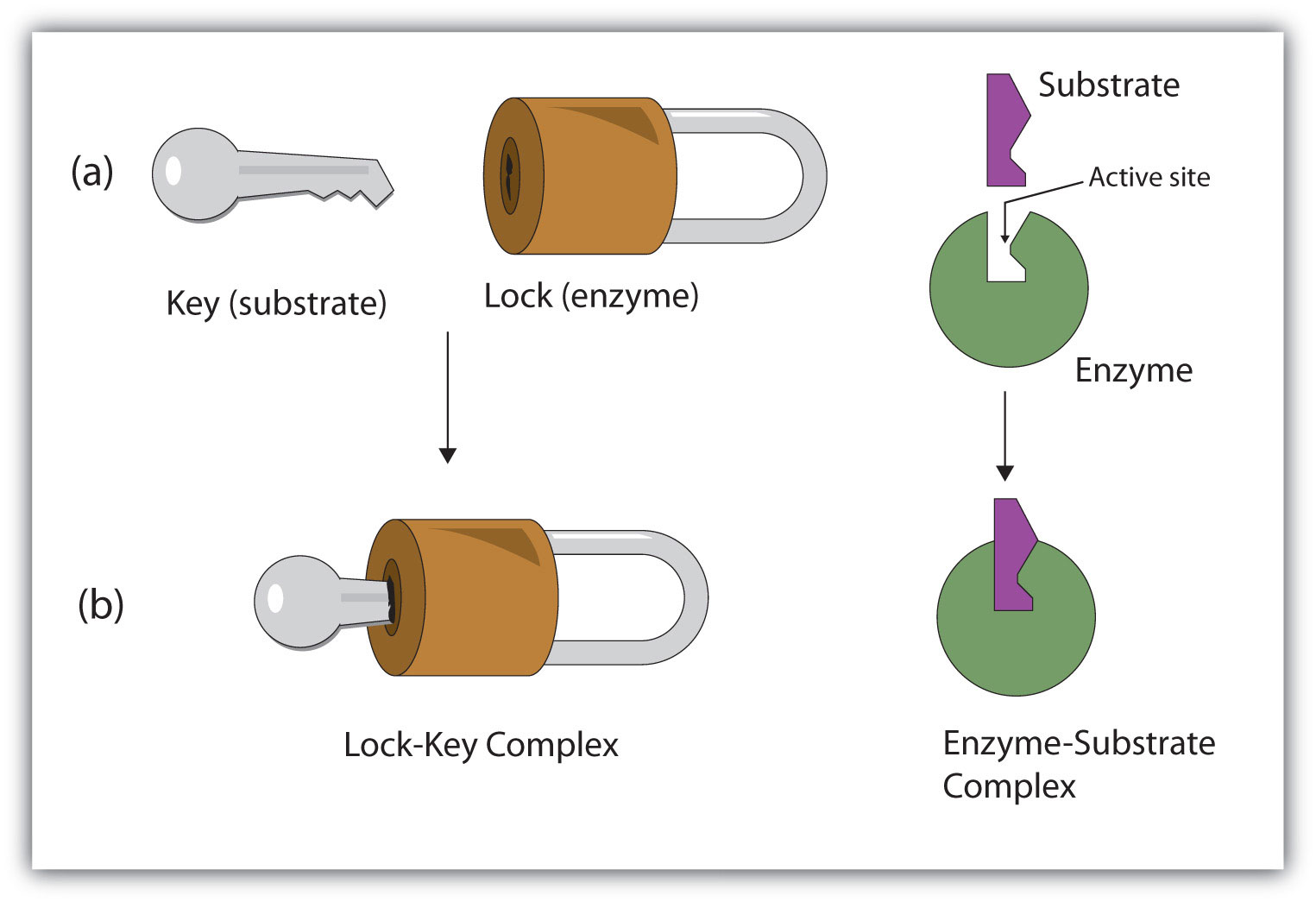
The compounds that enzymes act upon are known as substrates. The substrate which gets attached to the enzyme has a specific structure and that can only fit in a particular enzyme. When a substrate binds to a specific enzyme it is called an enzyme-substrate complex.
There a substrate binds the break down into various products. The part of the enzyme where the substrate binds is called the active site since thats where the catalytic action happens. An example of chemical digestion is the breakdown of blank into blank Nucleic acids into nucleotides The surface of the tongue is covered with blank stratified squamous epithelium and has bumps called blank where many taste buds can be found.
Enzymes bind with chemical reactants called substrates. The chemical or chemicals that an enzyme works on is called the ___ The part of the enzyme that the substrate fits into is called the ___. Of these five components pepsin is the principal enzyme involved in protein digestion.
Learn more about the fill-in-the-blank. When the enzyme has attached to the substrate the molecule is called the enzyme-substrate complex. This is an example of an anabolic enzyme reaction.
This occurs both in the digestive tract and at the cellular level. For example enzymes that break down proteins are called proteases. In some reactions a single-reactant substrate is broken down into multiple products.
This forms the enzyme-substrate complexThe reaction then occurs converting the substrate into products and forming an enzyme products complex. Chemicals called enzymes help your digestive tract and cells break down lipids but you cant use enzymes to force. There may be one or more substrates for each type of enzyme depending on the particular chemical reaction.
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water. A substrate enters the active site of the enzyme. Specific cells within the gastric lining known as chief cells release pepsin in an inactive form or zymogen form called pepsinogen.
For example the sugar found in milk is called lactose.

Influence Of The Temperature On The Enzyme Substrate Reaction Download Scientific Diagram

Enzyme Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

Pin By Samantha Seager On Anatomy Physiology Human Digestive System Digestive System Digestive System Anatomy

Fun Enzyme Doodle Notes Lesson Biology Activity Doodle Notes Biology Lessons
Chapter 6 Enzyme Principles And Biotechnological Applications Chemistry

Enzyme Substrate Complex Definition Examples Biology Dictionary

Cellular Aerobic Energy Production Also Known As Cellular Respiration Aerobic Oxidation And Oxidative Phosphorylation Cellular Respiration Oxidative Phosphorylation Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration

Exploring Enzymes Scientific American
18 6 Enzyme Action Chemistry Libretexts

Enzyme Structure And Function Article Khan Academy


Comments
Post a Comment